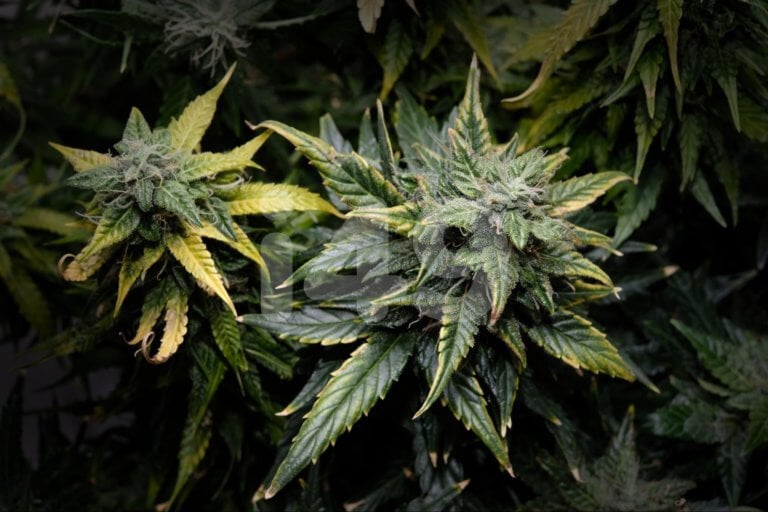
Ever wondered why your marijuana crops look dull and gloomy despite the top-shelf nutrients you feed them? As much as we’d like to raise our crops without hassle, it’s vital to know that cannabis deficiencies exist.
The ideal growing environment, check. Sufficient feed and water, check. A regular maintenance schedule, check. Why are the leaves still weak and turning yellow?
Marijuana crops rely on receiving just the right amount of minerals to grow into healthy bud-bearing beauties. A shortage or excess of nutes can harm your plant’s health.
Identifying and treating the various frailties on time is vital. Let’s discuss what happens to your plants when they experience a cannabis nutrient deficiency and how you can fix it.
Common cannabis deficiencies
When marijuana plants can’t access one or more of the essential nutrients for growth, they undergo deficiencies of those minerals. The absence of these elements severely impacts yield size, bud quality, and growth patterns.

When your plants are in distress, they show visible signs of what they’re lacking. Identify the symptoms early and use our cannabis deficiency guide to fix the problem.
Before we break down the various deficiencies your crops can experience, let’s first understand their biology. Like any other plant, marijuana needs sufficient supplements to sustain healthy growth. Weed crops rely on the availability of macro and micronutrients.
Cannabis plants require large quantities of macronutrients for primary microbial processes to occur during vegetation and flowering. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are the main minerals, along with iron (Fe), boron (B), and copper (Cu).
Marijuana crops use trace amounts of micronutrients to ensure the correct functioning of cellular anatomy. Weed deficiencies also surface from a lack of minerals like calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), silicon (Si), zinc (Zn), and sulfur (S).
Before adding or removing nutrients, check that the pH levels are what they’re supposed to be. Make use of a cannabis nutrient deficiency chart to keep the pH ranges on track.
Nutrient absorption happens at the roots. For this process to occur, the pH levels need to be on point for the specific growing medium. If the root environment is too acidic or alkaline, they won’t readily absorb the nutes. Ensure you have the best soil pH for cannabis growing.
Here’s an overview of the various pH ranges:
- Acidic pH: Lower than 7
- Alkaline pH: Higher than 7
- Ideal soil pH: 5.8–6.8
- Ideal hydroponics pH: 5.5–6.5
- Ideal water pH: 6.0–7.0
When the roots can’t absorb food, it causes a nutrient lockout and initiates a deficiency in cannabis plants.
Is a surplus of nutes a good or bad thing? While shortages cause harm to your crops, excesses don’t benefit them either. These nutrient toxicities result in the unfavorable accumulation of salts.
The symptoms of overfeeding are similar to shortages. The plants appear distressed and present discolored and droopy leaves.
Let’s take a brief look at the macro and micro cannabis deficiency charts, indicating how each shortage differs in terms of symptoms.
Macronutrient deficiencies
Macronutrients play a vital role in plant health. Various nute shortages may cause the following issues:
Nitrogen
- Yellowing of leaves
- Old leaves drop
- Tips burn on older leaves
- Stunted leaf growth
Potassium
- Yellowing of older leaves
- Young leaves wrinkle and curl under
- Development of necrosis
- Stems become brittle
- Growing tips die
Phosphorus
- Stunts leaf growth
- Dark green/purplish leaves and stems
- Hard/brittle stems
- Stunted root growth
Copper
- Leaves curl
- Wilting
Boron
- Tips burn in younger leaves
- Young leaves wrinkle and curl
- Growing tips die
Iron
- Yellowing of younger leaves
- Necrosis
Micronutrient deficiencies
Although marijuana plants need trace amounts of micronutrients, a lack of any may still cause problems like:
Calcium
- Leaves curl under
- Wilting
Magnesium
- Yellowing of older leaves and between veins
- Leaves curl over
- Necrosis
Manganese
- Yellowing of younger leaves and between veins
- Necrosis
Molybdenum
- Yellowing of middle leaves
- Young leaves wrinkle and curl
- Pale green leaf color
Sulfur
- Yellowing of upper leaves
Zinc
- Yellowing of older leaves
- Older leaf tips burn
- Young leaves wrinkle and curl
- Necrosis and mottling
Mobile vs. immobile nutrients in weed deficiencies
Cannabis supplements move through the plants as mobile and immobile elements.

Mobile nutrients move around and replenish areas that are lacking. Cannabis plant deficiencies associated with these minerals usually appear on the lower and older parts. You typically notice the first signs on the larger fan leaves.
A shortage of these mobile nutrients affects older leaves:
- Nitrogen
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Molybdenum
- Magnesium
As mobile nutrients travel, the lower half of the plant carries them from the bottom leaves to the top. If any part of the crop experiences a lack, the nutes move to those areas.
Immobile nutrients remain locked at the feeding spot. As a result, they don’t travel through the plant to replenish lost vitamins in areas showing signs of a cannabis deficiency.
Indications of immobile mineral shortages are present in the new growth of cannabis plants. These minerals are usually in the upper half of the crops and the outer branches. They include:
- Iron
- Zinc
- Sulfur
- Calcium
- Manganese
- Boron
- Copper
- Silicon
What causes weed plant deficiencies?
The absence of nutrients and an incorrect pH range at the root level causes marijuana plant deficiencies. The crops become stressed and can’t fight off mold, diseases, or pests and bugs.
When your growing medium’s pH range is out of balance, your plants experience a nutrient lockout. This hindrance eventually leads to a deficiency of one or more vital components needed for growth.
Are there ways to avoid shortages from occurring? Some growers agree that using organic supplements is the best way to stop these frailties before they occur. They break down microorganisms in the soil effortlessly for easy absorption.
Feed your crops with quality food and buy nutrients for cannabis plants that encourage successful growing rather than stunting them.
Identify and treat weed deficiencies
It’s vital to identify and treat weed plant deficiencies early. Marijuana crops need these nutrients to develop healthy leaves, branches, and buds.
Each shortage presents slightly different symptoms, which at times may seem similar. Correctly identifying each one allows you to provide the proper treatment as needed.
Let’s get into a bit more detail and break down each definition.
Calcium deficiency
When a calcium deficiency is present in your crops, their structure is crooked and prevents new growth. The lower leaves adapt to unusual curled shapes and have yellow with brownish spots and borders on the surface.

A shortage of calcium affects root health and causes the tips to die gradually. The result is stunted plant growth and slow recovery.
How to fix
Calcium plays an essential role in the structure of cannabis plants. It revives the cell walls and helps transport nitrogen and sugar throughout the plant. An excellent way to prevent a Ca deficiency is to add dolomite lime powder to your growing medium.
Once you’ve identified the problem, check if the pH levels are in the correct range. If you’re comfortable that the roots readily absorb food, it’s time to add some nutes.
Feed your marijuana crops with calcium and magnesium supplements. Make your own Ca/Mg supplements by blending a teaspoon of hydrated lime with a gallon of water.
Iron deficiency

Iron is the compound that helps cannabis plants produce chlorophyll. It’s an essential mineral for metabolic and energy-forming processes to occur. The roots won’t easily absorb Fe if the soil’s pH exceeds seven, causing a weed nutrient deficiency.
An iron deficiency usually surfaces with an imbalanced pH or if too many nutrients like zinc, manganese, and copper are present in the soil. Yellowing between the leaf veins is one of the first symptoms you can identify.
Interveinal chlorosis occurs at the base of new leaves and gradually moves to other foliage and older growth. An iron shortage is common when cultivating crops in coco coir or soil.
How to fix
To rid your crops of this problem, flush your growing medium with purified water. Doing this removes unwelcomed salts affecting the uptake of minerals while restoring the pH level. Iron is better absorbed in soil with a range of 6.0–6.5 and 5.5–6.5 in coco coir.
Provide your crops with the best cannabis nutrients containing the right amount of iron, calcium, magnesium, and quality soil.
Boron deficiency
Cannabis plants depend on small amounts of boron to form healthy cell walls and perform effective cell division. A boron deficiency is rare as most quality soils or composts contain sufficient quantities. It’s also a compound found in most tap water supplies.

The first signs of a boron shortage appear on new leaves with abnormally thick growth tips. The inner part turns yellow or brownish, along with spotting on the surface.
Inadequate amounts of this mineral also affect the plants’ structure, causing them to wilt. New leaves are stunted and grow slowly.
How to fix
Get rid of this deficiency by flushing your growing medium with clean pH water. Add a teaspoon of boric acid to a gallon of water to feed the plant. Boron is best absorbed into the roots when the pH ranges from 6.0–6.5 in soil and 5.5–6.2 in hydroponics.
This marijuana nutrient deficiency usually occurs when you use heavily filtered or reverse osmosis water. Provide the crops with enough moisture to adequately absorb this mineral.
Copper deficiency
Copper stimulates enzyme production in the roots of marijuana plants. It helps the crops use nitrogen, metabolize carbohydrates, and reduce oxygen. Coming across a copper deficiency is rare since most growing mediums and plant feeds contain this compound.

Copper marijuana deficiencies occur when the shoots of young leaves sag, then turn black and die. The tips of the leaves turn dark green to copper grey. New leaves begin twisting and continue to turn as they grow.
The leaves also have a dark blue or purple undertone, while the edges turn yellow. Other symptoms include slow growth, decreased yields, shiny leaves, and unripened buds.
Unbalanced pH ranges in the growing medium may cause a copper nutrient deficiency in weed plants. If it’s too high or low, it means the supplements aren’t accessing the roots.
How to fix
Flush your system with clean water at the correct pH levels. Soil absorbs copper well with a range of 6.0–7.0, while hydroponic systems require 5.5–6.5. Once flushed, give your plants the proper nutrients and be mindful of root care. The deficiency usually clears up within a week.
Magnesium deficiency
Magnesium is essential in producing chlorophyll on the leaves of marijuana crops. It harnesses the light for photosynthesis to take place.

When looking for superior nutrients, ensure they have ample magnesium. This compound allows enzymes to create carbohydrates and sugars to produce buds.
Magnesium deficiencies in marijuana plants start in new leaves at the lower half with yellowing spots that turn brown. You may also notice interveinal chlorosis in the older foliage as the veins begin to turn yellow.
You can only catch a magnesium deficiency 3–6 weeks after it starts in the plant. Brown spots develop on older leaves that become larger as the symptoms progress.
Mg shortages have been linked to the petioles presenting purplish or red tones. Leaves curl, die, and fall as the entire plant looks droopy.
How to fix
This deficiency usually surfaces when the pH range is too low and typically develops in a hydroponic setup. Keep the levels within your growing medium regulated at 5.5–5.8.
Add dolomite lime, magnesium sulfate, garden lime, or worm castings to your substrate. If you don’t have additives, Epsom salts work equally well.
Manganese deficiency
Marijuana plants need manganese to assist with vital cell functions like nitrogen use, respiration, and photosynthesis. The compound helps with root cell growth and protects it from harmful microbes. Too much iron or high pH levels usually cause a manganese deficiency.

Mn is an immobile nutrient, so a deficiency typically appears as chlorosis near the plant’s base. The discoloration spreads to the tips of the leaves while brown spots appear on older leaves. The margins and veins of the foliage appear green with yellow interveinal areas.
How to fix
Flushing your system with clean pH water eliminates this nutrient deficiency in cannabis plants. For successful manganese absorption, the ideal pH range for soil is 6.0–7.0 and 5.5–6.0 for hydroponics.
Yellow leaves with brown spots stop spreading to other parts within a week of treating the deficiency.
Molybdenum deficiency
Molybdenum is a micronutrient required by plants to convert nitrate to ammonium. The roots don’t easily absorb it if the pH range is too low. It’s one of the rarest cannabis deficiencies, but one to look out for and not leave unattended.

A molybdenum deficiency is easily detected when the color of the leaves’ edges changes to orange, red, or pinkish. This transition eventually spreads toward the center of the foliage. Leaves become droopy and distorted when the margins dry.
Old and middle-aged leaves turn yellow in colder weather and develop interveinal chlorosis. Look out for molted and spotted leaves too. The foliage cups and curls before completely twisting, which leads to leaves dying and dropping from the plant.
How to fix
If you catch this cannabis leaf deficiency early, immediately flush the medium with 6.0 pH water. Ensure the levels are ideal before feeding your crops again with nutrient solution. The roots absorb molybdenum well in soil with a pH range of 6.0–7.0 and 5.5–6.5 in hydroponics.
Have you got a molybdenum deficiency in the vegetative stage? Top your crops and remove dry and dead foliage. If the plants are in their flowering phase, remove leaf stems too to prevent bud mold. Successful recovery usually occurs by week three.
Phosphorus deficiency
Phosphorus is an essential mobile macronutrient required by cannabis plants to maintain their health and growth patterns. The crops utilize it to develop plant proteins and DNA, and it’s vital for photosynthesis. The plants need small amounts during vegging.

Sufficient amounts of phosphorus during germination and flowering are vital for your crops. Alkalinity in soil and insufficient drainage add to the development of this deficiency in weed plants.
A phosphorus deficiency is an uncommon shortage that mainly develops when pH levels are 7.0 and above. You can easily detect it in a hydroponic setup. Stunted growth, slow flowering, lower yields, and minimal resin production are symptoms of this nutrient shortage.
Look for the development of symptoms on the lower and older leaves in phosphorus pot plant deficiencies. They’re typically darker, shinier, and yellow in specific areas. Bronze, purple, or brown spots develop on the biggest leaves first. They become thick, dry, and stiff to the touch.
Reddish purple collations appear on the leaf stem. Leaves may also become dark blue or green, and dehydrated leaves curl up. If the deficiency is left unattended for too long, it slows the vertical and horizontal growth of the plant.
How to fix
Get rid of a phosphorus deficiency by checking the pH first, then flushing your medium with clean water. The ideal range for roots to absorb this nute is 6.2–7.0 in soil and 5.5–6.2 for hydro.
Restore the nutrients with quality fertilizer. Prune any discolored leaves and red stems. Don’t overwater your crops, and ensure that the growing temperature doesn’t exceed 68°F.
Silicon deficiency
Silicon nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants are common in hydroponic growing mediums. The micronutrient is available in most fertilizers and soils. Marijuana plants utilize Si to strengthen cellular walls and enable stable growth patterns.

A silicon deficiency develops when the leaves start to discolor, curl on the ends, and droop. Hindering root development causes it to become unhealthy, eventually encouraging stunted growth of the plant.
How to fix
Add diatomaceous earth to your crops to treat this deficiency. Use a foliar spray to revive the drooping leaves directly. Blend sodium silicate solution to your grow mix for the weak roots. Add potassium silicate solution to the fertilizer to repair the stunted growth.
Potassium deficiency
The roots of marijuana crops quickly and easily absorb potassium. This macronutrient is essential for the synthesis and transportation of sugars and carbohydrates. The plants need potassium to permit transpiration, root growth, and cell division.

A potassium deficiency in marijuana plants stresses them out, slows the growth rate, and reduces yields. Diagnosing the symptoms of this nutrient shortage takes a while and usually starts in a localized section of the plant.
A potassium nutrient deficiency in cannabis plants forces lower leaves to go brown and die. Older foliage suffers from chlorosis by paling out. The leaf tips and margins develop a rusty color (don’t confuse this with nutrient burn on cannabis leaves).
You may notice an increase in stems branching as they become brittle and weak. The brownish, yellow-edged leaves curl and present rusty brown spots on the surface.
The crops stretch more than usual but become susceptible to pests and diseases during the flowering stage, significantly slowing growth.
How to fix
If your pH range is correct, with soil at 6.0–7.0 or hydroponics at 5.5–6.5, it’s time to mend the feed. Adjust your fertilizer blends and add water-soluble potassium additives to fix deficiencies in cannabis plants.
Alternatively, add chicken manure, nute feeds rich in potassium, or foliar feeds like organic seaweed to your growing medium.
Sulfur deficiency
A lack of phosphorus usually causes a sulfur deficiency due to high pH levels in the root area.

This micronutrient is essential to the livelihood of cannabis plants for its ability to synthesize oils and terpenes. It’s also responsible for respiration, synthesis, and the breakdown of fatty acids.
Changes in new weed leaves show deficiencies in plants. The younger foliage at the back goes lime green before changing to yellow. Interveinal chlorosis and stunted growth are prominent symptoms of a lack of sulfur.
The small, thin, and fragile leaves become dry and brittle. The underpart of the foliage shows a pinkish, red, or orange color.
How to fix
Check the pH levels to ensure the roots absorb the mineral in the growing medium. The ideal range is 5.5–6.0. Add Epsom salts to clean water to feed your crops. Sprinkle an organic supplement over the soil. Once the deficiency clears, continue to provide a quality fertilizer.
Zinc deficiency
Marijuana crops need zinc to assist with the production of sugars and proteins. Plants use this compound to make chlorophyll and promote healthy stem growth. Zinc deficiencies in weed plants result from acidic pH levels, alkaline soil, and dry climates.

Younger leaves are first affected by a zinc deficiency. Newly developed parts of the crops show interveinal chlorosis. The blades become wrinkled, yellow, and distorted. Leaf tips are discolored and present a brownish burnt look.
You can identify a shortage of zinc by the rotated leaves. The plants stop growing vertically and display less internodal spacing. If your crops are flowering, the buds stop growing and may eventually die.
How to fix
Cure the deficiency by checking the pH first. Flush your system with purified water if the range isn’t at 6.0–6.5 for soil or 5.5–6.0 for hydroponics. The roots prefer absorbing zinc when the pH levels are more acidic.
Nitrogen deficiency
Nitrogen is one of the primary nutrients that marijuana plants rely on. A lack causes one of the most common weaknesses in cannabis. During vegetation, the plants need nitrogen to perform photosynthesis. This mobile compound travels from leaf to leaf.

A nitrogen deficiency mostly appears during the flowering phase, as the crops lose a lot of nutrients during this time. The first sign of this shortage appears on the older leaves of the plants. The foliage in the base and middle of the crops turns yellow and dies.
The fan leaves and surrounding foliage change to a pale yellow color. These weed leaf deficiencies affect the tips and edges, causing them to curl up while progressively losing shape. The foliage eventually becomes brown as it dries out and falls off the plant.
Discolored, dying leaves usually appear at the bottom of the plant before moving to the top.
How to fix
Check the pH range in your growing medium and use a nitrogen-rich foliar spray with supplements like seaweed or fish.
Remember that marijuana crops need different amounts of nitrogen at each growth stage. Provide more during the vegetative phase and feed less at flowering. The latter generally requires more nitrogen, so ensure you get the best nutrients for big buds.
It all stems from the root
Root health is the number one cause of cannabis nutrient deficiencies. You’ll notice changes when they can’t absorb the food they need to assist with plant growth. Correcting the pH range in your growing medium makes all the difference.
Look out for the signs and treat the problem from the bottom up. Remember to check your pH levels before adding or removing any nutes.
Growing cannabis is an enjoyable journey, don’t let these shortages kill your buzz or crops. Regularly follow a marijuana leaf deficiency chart to identify early signs of nutrient shortages.
Caught the problem too late? Get some more marijuana seeds and try again.